Common names from other countries
Classification / Names / Names
Common names | Synonyms | Catalog of Fishes (gen., sp.) | ITIS | CoL | WoRMS
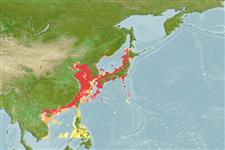
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Benthic; brackish; depth range 10 - 100 m (Ref. 3099). Subtropical; 46°N - 10°N, 106°E - 144°E
Western Pacific: from Vietnam to northern Japan, south to Bohol, Philippines. Introduced to Australia and New Zealand.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 9.6 range ? - ? cm Max length : 18.5 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3099)
Maximum depth from Ref. 80410. Demersal (Ref. 105264). Burrows in near-shore level-bottom substrates (Ref. 92) in sheltered embayment or estuaries (Ref. 3099). Occurs in muddy bottoms of bays and inlets (Ref. 105263). Feeds mainly on crustaceans, mollusks, polychaetes, and fish; occasionally on plant materials (Ref. 105093).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Some members of the order Stomatopoda pair for life and some come together only to mate. Males produce sperm ducts rather than spermatophores; females can brood a maximum of 50,000 eggs. Life cycle: Eggs hatch to a planktonic zoea which lasts for 3 months.
Manning, R.B. 1998. (Ref. 92)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
| FishSource | Sea Around Us
Tools
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref.
115969): 9.7 - 25.3, mean 15.8 (based on 374 cells).
Resilience
High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (K=0.72-0.82).
Vulnerability
Low vulnerability (10 of 100).