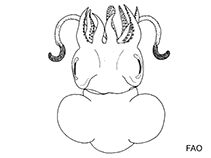
Euprymna scolopes Berry, 1913
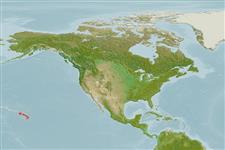
Hawaiian bobtail squid| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Euprymna scolopes AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Upload your photos
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Sepiolidae.
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Sepiolidae.
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
| Sepiida | Sepiolidae | Sepiolinae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range นิเวศวิทยา
; ระดับความลึก 0 - 1 m (Ref. 118073). Tropical; 25°N - 18°N, 170°W - 154°W
การแพร่กระจาย ประเทศต่างๆ | พื้นที่จำแนกตาม FAO | ระบบนิเวศหลายระบบ | การปรากฏขึ้น,การเกิดขึ้น,พบ | การแนะนำ
Eastern Central Pacific: Hawaiian Islands.
Length at first maturity / ขนาด / น้ำหนัก / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 3.0 cm ML เพศผู้/กระเทย; (Ref. 1695)
Adults have average mantle length of 2.5 cm. A model organism exhibiting short lifespan, rapid growth, and year-round availability (Ref. 118073). Small, benthic squid (Ref. 118073) found in shallow coastal waters (Refs. 843, 1695), living in muddy and sandy areas near seagrass meadows (Ref. 118075). Hosts a symbiotic luminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri, the sole bacterium found to naturally thrive in E. scolopes light organ. This symbiont colony reaches as much as 10^9 cells, and remains remarkably monospecific (Ref. 118072). The microbial colony serves as an antipredation measure for the squid, while the microbe gets shelter and nutrition from the squid. When E. scolopes forages at night, the bacterial colony emit light which matches the intensity of the moonlight above it, thus reducing the host's silhouette, preventing it from being eaten by predators in the ocean floor below (Ref. 118071). It also uses another form of camouflage by sticking sand grains to its body (Ref. 118075). A nocturnal predator, the squid finds shelter in the sand during the day and hunts at night over shallow-water sand flats (Ref. 118073). Mainly feeds on the shrimp Palaemon debilis but also consumes small worms (Ref. 122680).
Life cycle and mating behavior วัยเจริญพันธุ์ | การสืบพันธุ์ | การวางไข่ | เซลสืบพันธ์ของเพศเมีย(ไข่) | ความดกของไข่ | ตัวอ่อน
Members of the class Cephalopoda are gonochoric. Male and female adults usually die shortly after spawning and brooding, respectively. Mating behavior: Males perform various displays to attract potential females for copulation. During copulation, male grasp the female and inserts the hectocotylus into the female's mantle cavity where fertilization usually occurs. Life cycle: Embryos hatch into planktonic stage and live for some time before they grow larger and take up a benthic existence as adults.
Main reference
อ้างอิง | ผู้ประสานงาน | ผู้ร่วมมือ
Jereb, P. and C.F.E. Roper (eds.). 2005. (Ref. 1695)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
Data deficient (DD) ; Date assessed: 28 March 2009
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
การประมง: ไม่มีผลประโยชน์
| FishSource |
เครื่องมือ
ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ประเทศต่างๆ
พื้นที่จำแนกตาม FAO
ระบบนิเวศหลายระบบ
การปรากฏขึ้น,การเกิดขึ้น,พบ
การแนะนำ
Stocks
นิเวศวิทยา
อาหาร, โภชนาการ
รายการอาหาร
พื้นที่จำแนกตาม FAO
ระบบนิเวศหลายระบบ
การปรากฏขึ้น,การเกิดขึ้น,พบ
การแนะนำ
Stocks
นิเวศวิทยา
อาหาร, โภชนาการ
รายการอาหาร
ชื่อสามัญ
ชื่อพ้อง
ผู้ล่า
การสืบพันธุ์
วัยเจริญพันธุ์
การวางไข่
ความดกของไข่
เซลสืบพันธ์ของเพศเมีย(ไข่)
Egg development
ชื่อพ้อง
ผู้ล่า
การสืบพันธุ์
วัยเจริญพันธุ์
การวางไข่
ความดกของไข่
เซลสืบพันธ์ของเพศเมีย(ไข่)
Egg development
Age/Size
การเจริญเติบโต
Length-weight
Length-length
สัณฐานวิทยา
ตัวอ่อน
อุดมสมบรูณ์
การเจริญเติบโต
Length-weight
Length-length
สัณฐานวิทยา
ตัวอ่อน
อุดมสมบรูณ์
แหล่งที่มาจากอินเตอร์เน็ต
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | แผนภูมิชีวิตแบบต้นไม้ | Wikipedia (Go, ค้นหา) | บันทึกทางด้านสัตววิทยา
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref. 115969): 24.8 - 25.6, mean 25.3 (based on 36 cells).
Price category
(Ref. 80766):
Unknown.