Common names from other countries
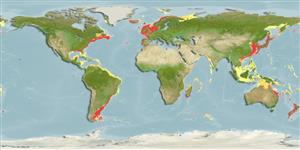
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Sinh thái học
; Mức độ sâu 1 - 134 m (Ref. 112705). Tropical
Indo-West Pacific and Atlantic Ocean.
Length at first maturity / Bộ gần gũi / Khối lượng (Trọng lượng) / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 1.0 cm TL con đực/không giới tính; (Ref. 125844)
Life cycle and mating behavior
Chín muồi sinh dục | Sự tái sinh sản | Đẻ trứng | Các trứng | Sự sinh sản | Ấu trùng
Members of the class Polychaeta are mostly gonochoric (sexual). Mating: Females produce a pheromone attracting and signalling the males to shed sperm which in turn stimulates females to shed eggs, this behavior is known as swarming. Gametes are spawned through the metanephridia or body wall rupturing (termed as "epitoky", wherein a pelagic, reproductive individual, "epitoke", is formed from a benthic, nonreproductive individual, "atoke"). After fertilization, most eggs become planktonic; although some are retained in the worm tubes or burrowed in jelly masses attached to the tubes (egg brooders). Life Cycle: Eggs develop into trocophore larva, which later metamorph into juvenile stage (body lengthened), and later develop into adults.
Salazar-Vallejo, S.I. 1996. (Ref. 7866)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Can't connect to MySQL database (slbapp). Errorcode: Too many connections