Common names from other countries
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
; profondeur 0 - 15 m (Ref. 112705). Tropical
Distribution
Pays | Zones FAO | Écosystèmes | Occurrences | Introductions
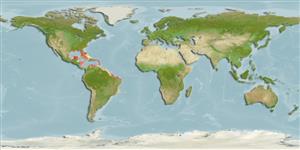
Western Central Atlantic: Central America to northern Brazil.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturité | Reproduction | Frai | Œufs | Fécondité | Larves
Members of the class Polychaeta are mostly gonochoric (sexual). Mating: Females produce a pheromone attracting and signalling the males to shed sperm which in turn stimulates females to shed eggs, this behavior is known as swarming. Gametes are spawned through the metanephridia or body wall rupturing (termed as "epitoky", wherein a pelagic, reproductive individual, "epitoke", is formed from a benthic, nonreproductive individual, "atoke"). After fertilization, most eggs become planktonic; although some are retained in the worm tubes or burrowed in jelly masses attached to the tubes (egg brooders). Life Cycle: Eggs develop into trocophore larva, which later metamorph into juvenile stage (body lengthened), and later develop into adults.
Salazar-Vallejo, S.I. 1996. (Ref. 7866)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
statut CITES (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Utilisations par l'homme
| FishSource |
Outils
Plus d'informations
Taille/Âge
Croissance
Longueur-poids
Longueur-longueur
Morphologie
Larves
Abondance
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Catégorie de prix
Unknown.