Common names from other countries
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecología
Asociado a arrecife; oceanodromo (Ref. 75927); rango de profundidad 0 - 347 m (Ref. 417), usually 0 - 100 m (Ref. 1977). Tropical; ? - 7°C (Ref. 275), preferred 26°C (Ref. 107945); 57°N - 38°S, 98°W - 146°E (Ref. 275)
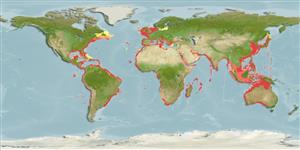
Distribución
Países | Áreas FAO | Ecosistemas | Ocurrencias, apariciones | Introducciones
Circumglobal in temperate and tropical seas.
Length at first maturity / Tamaño / Peso / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 8 - 11.3 cm Max length : 180 cm TL macho / no sexado; (Ref. 104052); 120 cm TL (female); peso máximo publicado: 10.0 kg (Ref. 275)
Maximum common depth is 150 m in Ref. 75927. Maximum depth range from Ref. 114857. Maximum length for female from Ref. 804. This octopus is taken by amateur fishers and in small to large-scale harvest throughout its range. The greatest fishery effort occurs off northwest Africa, and it is know as one of the most valuable octopod species throughout the Mediterranean Sea where it is marketed fresh or frozen (Ref. 96968).
Members of the class Cephalopoda are gonochoric. Male and female adults usually die shortly after spawning and brooding, respectively. Mating behavior: Males perform various displays to attract potential females for copulation. During copulation, male grasp the female and inserts the hectocotylus into the female's mantle cavity where fertilization usually occurs. Life cycle: Embryos hatch into planktonic stage and live for some time before they grow larger and take up a benthic existence as adults.
Roper, C.F.E., M.J. Sweeney and C.E. Nauen. 1984. (Ref. 275)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Human uses
Pesquerías: comercial
FAO - pesquerías: landings, species profile | FIRMS (Stock assessments) | FishSource | Sea Around Us
Herramientas
Fuentes de Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref.
115969): 10 - 28.9, mean 25.8 (based on 8514 cells).
Resiliencia
Alto, población duplicada en un tiempo mínimo inferior a 15 meses (K=0.38-0.72; tm=1.2).
Prior r = 0.77, 95% CL = 0.51 - 1.15, Based on 4 full stock assessments.
Vulnerability
Moderate to high vulnerability (48 of 100).