Favia fragum (Esper, 1793)
Golfball coral| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
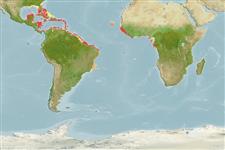
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Favia fragum AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Faviidae.
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Hexacorallia | Scleractinia | Faviidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Reef-associated; depth range 0 - 30 m (Ref. 848). Subtropical; 33°N - 25°S, 92°W - 12°E (Ref. 848)
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Atlantic Ocean.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 5.0 cm COLD male/unsexed; (Ref. )
Short description Morphology
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Collin, R., M.C. Díaz, J. Norenburg, R.M. Rocha, J.A. Sánchez, M. Schulze, A. Schwartz and A. Valdés 2005 Photographic identification guide to some common marine invertebrates of Bocas Del Toro, Panama. Caribbean Journal of Science. 41(3):638-707. (Ref. 415)
IUCN Red List Status
(Ref. 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Diet composition
Food consumption
Predators
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Abundance
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record