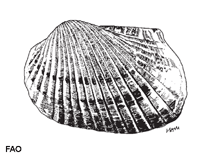
Scapharca indica (Gmelin, 1791)
Rudder ark| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
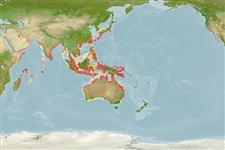
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Scapharca indica AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Arcida | Arcidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Benthic; depth range 0 - 25 m (Ref. 348). Tropical
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Indo-West Pacific. Climate: tropical to subtropical.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 5.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 348); common length : 4.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 348)
Short description Morphology
Shell solid, laterally compressed and subrectangular in shape, very inequilateral, much longer than high and wider posteriorly; slightly inequivalve, left valve somewhat overlapping the right valve on posteroventral margin. Umbones small and situated anteriorly, cardinal area long and narrow. About 28 radial ribs (25 to 33) at each valve; ribs low and flat, wider than the interstices, slightly granulated on the anterior part of left valve. Periostracum coarse, concentrically striated. Internal margins with crenulations corresponding with the external radial ribs. No byssal gape. Colour: outside of shell whitish under the blackish brown periostracum. Inner side white, often tinged pale grey at periphery.
This species is considered to have a wide range, but the relationship between the Indian Ocean and West Pacific forms is insufficiently known (Ref. 348).
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Bivalvia are mostly gonochoric, some are protandric hermaphrodites. Life cycle: Embryos develop into free-swimming trocophore larvae, succeeded by the bivalve veliger, resembling a miniature clam.
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Poutiers, J.M. 1998. (Ref. 348)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Trophic Ecology
Food items
Diet
Food consumption
Ration
Predators
Diet
Food consumption
Ration
Predators
Ecology
Population dynamics
Growth
Age/Size
Length-weight
Length-length
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Recruitment
Abundance
Age/Size
Length-weight
Length-length
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Recruitment
Abundance
Life cycle
Distribution
Human Related
Aquaculture profile
Stamps, Coins Misc.
Stamps, Coins Misc.
Outreach
References
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref. 115969): 22.5 - 29.2, mean 28.6 (based on 2384 cells).
Price category
(Ref. 80766):
Unknown.