Acanthocardia aculeata (Linnaeus, 1758)
Spiny cockle| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
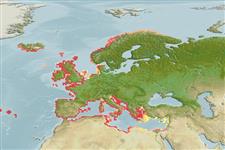
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Acanthocardia aculeata AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Cardiida | Cardiidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Benthic; depth range 5 - 30 m (Ref. 2758). Temperate; 54°N - 30°N, 11°W - 36°E
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Northeast Atlantic and the Mediterranean: from Celtic and Lusitanian provinces, extending into the Mediterranean.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 10.2 cm SHL male/unsexed; (Ref. 360); common length : 7.6 cm SHL male/unsexed; (Ref. 360)
Short description Morphology
Shell: solid, convex valves, equivalve and inequilateral, roughly oval in shape, uniformly deep yellow brown in color; sculpture consists of 20-22 well-developed ribs, with triangular spikes along the mid-line, in between are very marked concentric grooves; external ligament behind the umbones, hinge is heterodont; inside the valves are two identical scars (dimyarian and isomyarian) joined by a continuous pallial line, lacking a sinus. Body: foot is roughly cylindrical, well developed and used for leaping on the sand; distal extremity is bright red.
Minimum depth from Ref. 2703. Maximum depth from Ref. 106644.
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Bivalvia are mostly gonochoric, some are protandric hermaphrodites. Life cycle: Embryos develop into free-swimming trocophore larvae, succeeded by the bivalve veliger, resembling a miniature clam.
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Gaspar, M.B., M.N. Santos and P. Vasconcelos. 2001. (Ref. 2758)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Trophic Ecology
Food items
Diet
Food consumption
Ration
Predators
Diet
Food consumption
Ration
Predators
Ecology
Population dynamics
Life cycle
Distribution
Human Related
Outreach
References
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref. 115969): 8.5 - 21.3, mean 17.8 (based on 884 cells).



