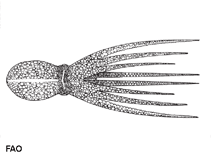
Amphioctopus aegina (Gray, 1849)
Sandbird octopus| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
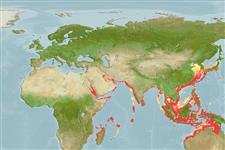
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Amphioctopus aegina AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Cephalopoda | Octopoda | Octopodidae | Octopodinae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Benthic; depth range 30 - 120 m (Ref. 275). Tropical; 41°N - 24°S, 32°E - 143°E (Ref. 275)
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Indo-West Pacific: from Mozambique to Red Sea and Japan.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 10.0 cm ML male/unsexed; (Ref. 275); max. published weight: 400.00 g (Ref. 275)
Short description Morphology
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Roper, C.F.E., M.J. Sweeney and C.E. Nauen 1984 FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 3. Cephalopods of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species of interest to fisheries. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(3):277p. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 275)
IUCN Red List Status
(Ref. 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Threat to humans
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Diet composition
Food consumption
Predators
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Abundance
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record