Leukoma thaca (Molina, 1782)
Taca clam| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Leukoma thaca AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Upload your photos
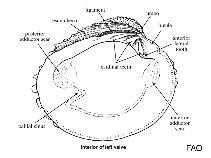
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Veneridae.
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Veneridae.
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Venerida | Veneridae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Benthic; depth range 0 - 20 m (Ref. 101272). Temperate, preferred 18°C (Ref. 107945); 16°S - 47°S, 110°W - 70°W
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Southeast Pacific: Chile, Easter Island, and Peru. Subtropical to temperate.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 8.0 cm SHL male/unsexed; (Ref. 101426)
Common shell length is between 5 to 7 cm (Ref. 101426). Subtidal, living just below the surface of sandy substrates. Also found intertidally in mud and gravel (Ref. 116664). Has high lethal temperature threshold, surviving El Niño events (Ref. 105334). In general, suspension feeding bivalves mainly depend on phytoplankton and detritus material for nutrition (Ref. 107088).
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Bivalvia are mostly gonochoric, some are protandric hermaphrodites. Life cycle: Embryos develop into free-swimming trocophore larvae, succeeded by the bivalve veliger, resembling a miniature clam.
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Urban, H.J. and B. Campos. 1994. (Ref. 75339)
IUCN Red List Status
(Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
FAO - Fisheries: landings, species profile | FishSource | Sea Around Us
Tools
More information
Trophic Ecology
Ecology
Population dynamics
Growth
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Recruitment
Abundance
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Recruitment
Abundance
Life cycle
Distribution
Human Related
Aquaculture profiles
Stamps, coins, misc.
Stamps, coins, misc.
Outreach
Taxonomy
References
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Fisheries: species profile; publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Nutrients : Calcium = 149 [71, 228] mg/100g; Iron = 8.53 [1.95, 15.11] mg/100g; Protein = 9.88 [8.64, 11.12] %; Omega3 = 0.313 [0.202, 0.423] g/100g; Selenium = 61 [50, 72] μg/100g; VitaminA = 0 μg/100g; Zinc = 2.04 [0.56, 3.51] mg/100g (wet weight); based on nutrient studies.