Kuphus polythalamia (Linnaeus, 1767)
| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |

|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Kuphus polythalamia AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
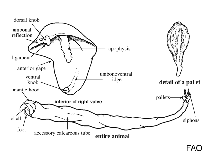
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Teredinidae.
Classification / Names Tên thường gặp | Các synonym ( Các tên trùng) | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Myida | Teredinidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / Mức độ sâu / distribution range Sinh thái học
. Subtropical
Distribution Các nước | Các khu vực của FAO | Các hệ sinh thái | Những lần xuất hiện | Những chỉ dẫn
Indo-Pacific.
Length at first maturity / Bộ gần gũi / Weight / Age
Chín muồi sinh dục: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Life cycle and mating behavior Chín muồi sinh dục | Sự tái sinh sản | Đẻ trứng | Eggs | Sự sinh sản | Larvae
Main reference
Các tài liệu tham khảo | Người điều phối | Người cộng tác
Bernard, F.R., Y.Y. Cai and B. Morton 1993 Catalogue of the living marine bivalve molluscs of China. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. 121 p. (Tài liệu tham khảo 75831)
IUCN Red List Status
(Tài liệu tham khảo 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Tài liệu tham khảo 108899)
CMS (Tài liệu tham khảo 116361)
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Các công cụ
Thêm thông tin
Thành phần thức ăn
Thành phần thức ăn
Các động vật ăn mồi
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Sự phong phú
Các nguồn internet
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Cây Đời sống | Wikipedia (Go, tìm) | Tạp chí Zoological Record